Explain Holocene

Holocene Technical Terms
Holocene: The epoch of the Quaternary Period of geologic time following the Pleistocene Epoch (from the present to about 10 to 12 thousand years ago); also corresponding (time-stratigraphic) “series” of earth materials. SW
Remember Hogback

Hogback Technical Terms
Hogback: A sharp-crested, symmetric ridge formed by highly tilted resistant rock layers; a type of homocline produced by differential erosion of interlayered resistant and weak rocks with dips greater than about 25 o (or approximately > 45 % slopes). Compare – homoclinal ridge, cuesta. SW & HP
Expose Hillslope Terrace

Hillslope Terrace Technical Terms
Hillslope Terrace: A raised, generally horizontal strip of earth and/or rock bounded by a down-slope berm or retaining wall, constructed along a contour on a hillslope to make land suitable for tillage and to prevent accelerated erosion; common in steep terrain, both archaic (e.g. Peru) and modern (e.g. Nepal).
Expose Hillslope-Profile Position

Hillslope-Profile Position Technical Terms
Hillslope-Profile Position: Discrete slope segments found along a transect line that runs perpendicular to the contour, beginning at a divide and descending to a lower, bounding stream channel or valley floor; a discrete piece of a two-dimensional cross profile of a hill. Positions are commonly separated from one another by inflection points along the line. In descending elevational order, the hillslope-profile positions of a simple hillslope include summit, shoulder, backslope, footslope, and toeslope. Not all of these segments (positions) are necessarily present along a particular hillslope. Complex hillslopes include multiple sequences or partial sequences, or partial sequences. Compare - geomorphic components - hills. SW, HP, & RR
Expose Hillslope
Hillslope Technical Terms
Hillslope: A generic term for the steeper part of a hill between its summit and the drainage line, valley flat, or depression floor at the base of the hill. Compare – mountain slope. HP
Explain Hillock

Hillock Technical Terms
Hillock: A generic name for a small, low hill, generally between 3 – 30 m in height and slopes between 5 and 50% (e.g., bigger than a mound but smaller than a hill); commonly considered a microfeature. Compare – mound, hill. SW
Explain Hill

Hill Technical Terms
Hill: A generic term for an elevated area of the land surface, rising at least 30 m (100 ft.) to as much as 300 meters (approx. 1000 ft.) above surrounding lowlands, usually with a nominal summit area relative to bounding slopes, a well-defined, rounded outline and slopes that generally exceed 15 percent. A hill can occur as a single, isolated mass or in a group. A hill can be further specified based on the magnitude of local relief: low hill (30 – 90 m) or high hill (90 - 300 m). Informal distinctions between a hill and a mountain are often arbitrary and dependent on local convention. Compare - hillock, plateau, mountain, foothills, hills. SW & HP
Discover Highmoor Bog

Highmoor Bog Technical Terms
Highmoor Bog: A bog, often on the uplands, whose surface is covered by sphagnum mosses which, because of their high degree of water retention, make the bog more dependent upon precipitation than on the water table. The bog often occurs as a raised peat bog or blanket bog. Compare - lowmoor bog, raised bog. GG
Expose High Hill

High Hill Technical Terms
High Hill: A generic name for an elevated, generally rounded land surface with high local relief, rising between 90 meters (approx. 300 ft.) to as much as 300 m (approx. 1000 ft.) above surrounding lowlands. Compare – low hill, hill, hillock. SW
Remember High-Center Polygon

High-Center Polygon Technical Terms
High-Center Polygon: A polygon whose center is raised relative to its boundary. Compare - low center polygon. NRC
Explain Herbaceous Peat
Herbaceous Peat Technical Terms
Herbaceous Peat: An accumulation of organic material, decomposed to some degree that is predominantly the remains of sedges, reeds, cattails and other herbaceous plants. Compare - moss peat, sedimentary peat, woody peat, peat, muck, and mucky peat. SSM
Explain Headwall

Headwall Technical Terms
Headwall: A steep slope at the head of a valley; e.g. the rock cliff at the back of a cirque. Compare – cirque headwall. GG
Expose Head Slope
Head Slope Technical Terms
Head Slope: A geomorphic component of hills consisting of a laterally concave area of a hillside, especially at the head of a drainageway, resulting in converging overland water flow (e.g. sheet wash); head slopes are dominated by colluvium and slope wash sediments (e.g., slope alluvium); contour lines form concave curves. Slope complexity (downslope shape) can range from simple to complex. Headslopes are comparatively moister portions of hillslopes and tend to accumulate sediments (e.g., cumulic profiles) where they are not directly contributing materials to channel flow. Compare - side slope, nose slope, free face, interfluve, crest, base slope. SW.
Remember Head-Of-Outwash

Head-Of-Outwash Technical Terms
Head-Of-Outwash: A sloping and sometimes high relief landform composed predominantly of glaciofluvial sediment that delimits a former ice-margin of a relatively static, rapidly wasting glacier. A steep ice-contact slope forms the ice-proximal face of the landform; a more gently sloping surface dips away on the distal slope, if not slumped. Compare – ice-margin complex. SW
Remember Headland
Headland Technical Terms
Headland: (a) An irregularity of land, especially of considerable height with a steep cliff face, jutting out from the coast into a large body of water (usually the sea or a lake); a bold promontory or a high cape. (b) The high ground flanking a body of water, such as a cove. (c) The steep crag or cliff face of a promontory. GG
Discover Head

Head Technical Terms
Head: The source, beginning, or upper part of a stream. (b) The upper part or end of a slope or valley. GG
Expose Hanging Valley

Hanging Valley Technical Terms
Hanging Valley: A tributary valley whose floor at the lower end is notably higher than the floor of the main valley in the area of junction. GG
Expose Half Graben

Half Graben Technical Terms
Half Graben: An elongate, structural trough or basin bounded on one side by a normal fault. It may or may not produce a topographic basin. Compare – graben. GG
Discover Gut

Gut Technical Terms
Gut: A gully, ravine, small valley, or narrow passage on land. (b) [stream] (not preferred – use tidal channel). A tidal stream connecting two larger waterways within a lagoon, estuary or bay. SW & GG
Discover Gully

Gully Technical Terms
Gully: A small channel with steep sides caused by erosion and cut in unconsolidated materials by concentrated but intermittent flow of water usually during and immediately following heavy rains or ice / snow melt. A gully generally is an obstacle to wheeled vehicles and too deep (e.g., > 0.5 m) to be obliterated by ordinary tillage; (a rill is of lesser depth and can be smoothed over by ordinary tillage). Compare - rill, ravine, arroyo, swale, draw. HP & GSST
Remember Gulf

Gulf Technical Terms
Gulf: A relatively large part of an ocean or sea extending far into the land, partly enclosed by an extensive sweep of the coast, and opened to the sea through a strait (e.g. Gulf of Mexico); the largest of various forms of inlets of the sea. It is usually larger, more enclosed, and more deeply indented than a bay. Compare – bay. GG
Expose Gulch

Gulch Technical Terms
Gulch: A small stream channel, narrow and steep-sided in cross section, and larger than a gully, cut in unconsolidated materials. General synonym - ravine. Compare - arroyo, draw, gully, wash. HP
Remember Grus

Grus Technical Terms
Grus: The fragmental products of in situ granular disintegration of granite and granitic rocks, dominated by inter-crystal disintegration. Compare - saprolite. SW & GG
Remember Ground Soil

Ground Soil Technical Terms
Ground Soil: Any soil at the present-day land surface and actively undergoing pedogenesis, regardless of its history (i.e., relict, exhumed). Compare – buried soil. SW & RR
Expose Flat

Flat Technical Terms
Flat: (a) (adjective) Said of an area characterized by a continuous surface or stretch of land that is smooth, even, or horizontal, or nearly so, and that lacks any significant curvature, slope, elevations, or depressions. (b) (noun) An informal, generic term for a level or nearly level surface or small area of land marked by little or no local relief. Compare - mud flat. (c) (not recommended) A nearly level region that visibly displays less relief than its surroundings. GG.
Expose Flatwoods

Flatwoods Technical Terms
Flatwoods : Broad, low gradient (generally < 1 % slope but up to 2% near drainageways), low relief interstream areas and characterized by non-hydric, poorly drained soils (seasonal saturation or water table) at depths of 15 -45 cm (6 – 18”), and naturally forested by pines that dominate the Lower Coastal Plain of the southeastern US. Regional differences occur in dominant vegetation and soil material (e.g. in south Florida, soils are dominantly sandy Spodosols and the understory is dominantly saw palmetto). Hydropedologically and elevationally this landform occurs slightly above minor depressions (which have a seasonal water table at or above the surface), drainageways, and drainhead complexes, but lies below better drained and slightly higher small rises or knolls. Generally they are most extensive toward the interiors of low, broad interstream divides and away from drainageways. SW
Explain Flood Plain

Flood Plain Technical Terms
Flood Plain: The nearly level plain that borders a stream and is subject to inundation under flood-stage conditions unless protected artificially. It is usually a constructional landform built of sediment deposited during overflow and lateral migration of the streams. HP
Expose Flood-Plain Landforms

Flood-Plain Landforms Technical Terms
Flood-Plain Landforms: A variety of constructional and erosional features produced by stream channel migration and flooding, e.g., backswamp, braided stream, flood-plain splay, meander, meander belt, meander scroll, oxbow lake, and natural levee. HP
Discover Flood-Plain Playa

Flood-Plain Playa Technical Terms
Flood-Plain Playa: A landform consisting of very low gradient, broad, barren, axial-stream channel segments in an intermontane basin. It floods broadly and shallowly and is veneered with barren fine-textured sediment that crusts. Commonly, a flood-plain playa is segmented by transverse, narrow bands of vegetation, and it may alternate with ordinary narrow or braided channel segments. FFP
Explain Flood-Plain Splay

Flood-Plain Splay Technical Terms
Flood-Plain Splay: A fan-shaped deposit or other outspread deposit formed where an overloaded stream breaks through a levee (natural or artificial) and deposits its material (often coarse-grained) on the flood plain. Compare - crevasse. GG
Discover Flood-Plain Step

Flood-Plain Step Technical Terms
Flood-Plain Step: An essentially flat, terrace-like alluvial surface within a valley that is frequently covered by flood water from the present stream (e.g., below the 100 year flood level); any approximately horizontal surface still actively modified by fluvial scour and/or deposition (i.e., cut and fill and/or scour and fill processes). May occur individually or as a series of steps. Compare – stream terrace. SW & RR
Expose Flood-Tidal Delta

Flood-Tidal Delta Technical Terms
Flood-Tidal Delta: A largely subaqueous (sometimes intertidal), crudely fan-shaped deposit of sand-sized sediment formed on the landward side of a tidal inlet (modified from Boothroyd et al., 1985; Davis, 1994; Ritter et al., 1995). Flood tides transport sediment through the tidal inlet and into the lagoon over a flood ramp where currents slow and dissipate (Davis, 1994). Generally, flood-tidal deltas along microtidal coasts are multi-lobate and unaffected by ebbing currents (modified from Davis, 1994). Compare – flood-tidal delta slope. SSS
Explain Flood-Tidal Delta Flat

Flood-Tidal Delta Flat Technical Terms
Flood-Tidal Delta Flat: The relatively flat, dominant component of the flood-tidal delta. At extreme low tide this landform may be exposed for a relatively short period (modified from Boothroyd et al., 1985). SSS
Discover Flood-Tidal Delta Slope

Flood-Tidal Delta Slope Technical Terms
Flood-Tidal Delta Slope: An extension of the flood-tidal delta that slopes toward deeper water in a lagoon or estuary, composed of flood channels, inactive lobes (areas of the flood-tidal delta that are not actively accumulating sand as a result of flood tides), and parts of the terminal lobe of the flood-tidal delta (modified from Boothroyd et al., 1985). SSS
Explain Floodway
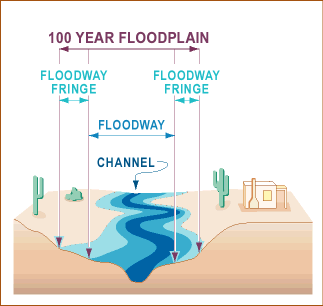
Floodway Technical Terms
Floodway: a) A large-capacity channel constructed to divert floodwaters or excess streamflow from populous, flood-prone areas, such as a bypass route bounded by levees. b) The part of the flood plain kept clear of encumbrances and reserved for emergency diversion of floodwaters. GG
Remember Floor

Floor Technical Terms
Floor: (a) A general term for the nearly level, lower part of a basin or valley; (not preferred) refer to basin floor, valley floor, (b) The bed of any body of water; e.g., the nearly level surface beneath the water of a stream, lake, or ocean. GG
Remember Flow

Flow Technical Terms
Flow: A category of mass movement processes, associated sediments (flow deposit) and landforms characterized by slow to very rapid downslope movement of unconsolidated material which, whether saturated or comparatively dry, behaves much as a viscous fluid as it moves. Types of flows can be specified based on the dominant particle size of sediments (i.e. debris flow (e.g., lahar), earth flow (creep, mudflow), rock fragment flow (e.g., rockfall avalanche), debris avalanche]. Compare - fall, topple, slide, lateral spread, complex landslide, landslide. SW & DV
Expose Flowtill

Flowtill Technical Terms
Flowtill: A till, commonly supraglacial that is modified and transported by plastic mass flow; also spelled flow till. Compare - ablation till, basal till, lodgment till, mass-movement till, slump-till, supraglacial melt-out till. GG
Expose Flute

Flute Technical Terms
Flute: A lineation or streamlined furrow or ridge parallel to the direction of ice movement, formed in newly deposited till or older drift. They range in height from a few centimeters to 25 m, and in length from a few meters to 20 km. Compare – glacial groove. GG
Explain Fluve

Fluve Technical Terms
Fluve: A roughly linear or elongated depression (topographic low) of any size, along which water flows, at some time. Compare - interfluve. FFP & SW.
Explain Fluvial

Fluvial Technical Terms
Fluvial: Of or pertaining to rivers or streams; produced by stream or river action. Compare – alluvial, colluvial. HP
Explain Fluviokarst

Fluviokarst Technical Terms
Fluviokarst: A karst landscape dominated by both 1) karst features (deranged and subsurface drainage, blind valleys, swallow holes, large springs, closed depressions, and caves), generally limited to low-lying interfluve areas, and 2) surface drainage by large rivers, with associated fluvial features (adjacent stream terraces) and sediments (alluvium), that commonly maintain their surface courses and are fed by underground tributaries; the dominant karst in the eastern USA. Compare – sinkhole karst, pavement karst, glaciokarst, karst. SW, WW, & GG
Discover Fluviomarine Bottom

Fluviomarine Bottom Technical Terms
Fluviomarine Bottom: The nearly level or slightly undulating, relatively low-energy, depositional environment with relatively deep water (1.0 to >2.5 m) directly adjacent to an incoming stream and composed of interfingered and mixed fluvial and marine sediments (fluviomarine deposits). SSS
Expose Fluviomarine Deposit

Fluviomarine Deposit Technical Terms
Fluviomarine Deposit: Stratified materials (clay, silt, sand, or gravel) formed by both marine and fluvial processes, resulting from non-tidal sea level fluctuations, subsidence and/or stream migration (i.e. materials originally deposited in a nearshore environment and subsequently reworked by fluvial processes as sea level fell). Compare – estuarine deposit, lacustrine deposit, lagoonal deposit, marine deposit, overbank deposit. SW
Discover Fluviomarine Terrace
Fluviomarine Terrace Technical Terms
Fluviomarine Terrace: A constructional coastal strip, sloping gently seaward and/or down valley, veneered or completely composed of fluviomarine deposits (typically silt, sand, fine gravel). Compare – terrace, stream terrace, marine terrace. SW
Remember Fly Ash

Fly Ash Technical Terms
Fly Ash: All particulate matter that is carried in a gas stream, especially in stack gases at a coal-fired plant for the generation of electric power; also name given to sediments from the same source, stock piled in settling ponds or spoil piles. SW & GG
Explain Foothills

Foothills Technical Terms
Foothills: A steeply sloping upland composed of hills with relief of 30 up to 300 meters and fringes a mountain range or high-plateau escarpment. Compare - hill, mountain, plateau. SW & HP
Expose Footslope

Footslope Technical Terms
Footslope: The hillslope profile position that forms the concave surface at the base of a hillslope. It is a transition zone between upslope sites of erosion and transport (shoulder, backslope) and downslope sites of deposition (toeslope). Compare - summit, shoulder, backslope, and toeslope. SW
Expose Foredune

Foredune Technical Terms
Foredune: A coastal dune or dune ridge oriented parallel to the shoreline, occurring at the landward margin of the beach, along the shoreward face of a beach ridge, or at the landward limit of the highest tide, and more or less stabilized by vegetation. GG
Expose Formation

Formation Technical Terms
Formation: The basic lithostratigraphic unit in the local classification of rocks. A body of rock (commonly a sedimentary stratum or strata, but also igneous and metamorphic rocks) generally characterized by some degree of internal lithologic homogeneity or distinctive lithologic features (such as chemical composition, structures, textures, or general kind of fossils), by a prevailing (but not necessarily tabular) shape, and is mappable at the earth's surface (at scales of the order of 1:25,000) or traceable in the subsurface. Formation may be combined into Groups or subdivided into members. Compare - bed. HP

