Explain Buried Soil

Buried Soil Technical Terms
Buried Soil: Soil covered by an alluvial, loessal, or other earthy mantle of more recent material, typically to depths exceeding 50 cm; recent surface deposits < 50 cm thick are generally considered as part of the ground soil. Compare - ground soil, exhumed, relict,. GSST & ST
Discover Buried

Buried Technical Terms
Buried: Landforms, geomorphic surfaces, or paleosols covered by younger sediments (e.g. eolian, glacial, and alluvial). Compare - exhumed, relict. HP
Explain Burial Mound

Burial Mound Technical Terms
Burial Mound: A small human-made hill, composed of debris accumulated during successive occupations of the site, or of earth heaped up to mark a burial site; also called mound. GG
Discover Broad Interstream Divide
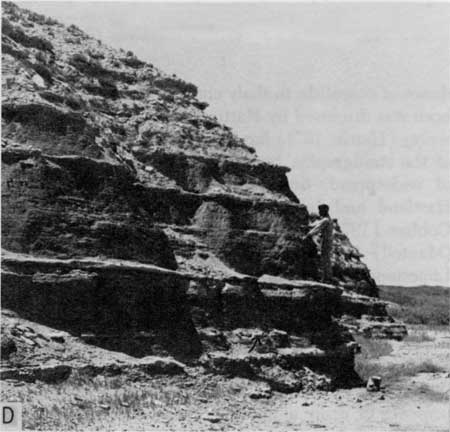

Broad Interstream Divide Technical Terms
Broad Interstream Divide: A type of very wide, low gradient (level to nearly level) interfluve that lacks a well developed drainage network such that large portions of the local upland lack stream channels or other drainageways; extensive in lower coastal plains and some lake plains, till plains and alluvial plain remnants. Compare – interfluve. SW & RD
Discover Broad Interstream Divide

Broad Interstream Divide Technical Terms
Broad Interstream Divide: A type of very wide, low gradient (level to nearly level) interfluve that lacks a well developed drainage network such that large portions of the local upland lack stream channels or other drainageways; extensive in lower coastal plains and some lake plains, till plains and alluvial plain remnants. Compare – interfluve. SW & RD
Remember Breccias

Breccias Technical Terms
Breccias: A coarse-grained, clastic rock composed of angular rock fragments (larger than 2 mm) commonly bonded by a mineral cement in a finer-grained matrix of varying composition and origin. The consolidated equivalent of rubble. Compare - conglomerate. GSST
Discover Braided Stream
Braided Stream Technical Terms
Braided Stream: A channel or stream with multiple channels that interweave as a result of repeated bifurcation and convergence of flow around inter-channel bars, resembling (in plan view) the strands of a complex braid. Braiding is generally confined to broad, shallow streams of low sinuosity, high bed load, non-cohesive bank material, and a steep gradient. At a given bank-full discharge, braided streams have steeper slopes and shallower, broader, and less stable channel cross sections than meandering streams. Compare - meandering channel, flood-plain landforms. HP
Explain Box Canyon

Box Canyon Technical Terms
Box Canyon: a) A narrow gorge or canyon containing an intermittent stream following a zigzag course, characterized by high, steep rock walls and typically closed upstream by a similar wall, giving the impression, as viewed from its bottom, of being surrounded or “boxed in” by almost vertical walls. b) A steep-walled canyon heading against a cliff a dead-end canyon. GG
Remember Bottomland

Bottomland Technical Terms
Bottomland: use flood plain. An obsolete, informal term loosely applied to varying portions of a flood plain. SW
Discover Borrow Pit

Borrow Pit Technical Terms
Borrow Pit: An excavated area from which earthy material has been removed typically for construction purposes offsite; also called barrow pit. GG
Discover Bomb

Bomb Technical Terms
Bomb: 64 mm in at least one dimension that was ejected while still viscous and solidified into it’s rounded form in flight. Compare - block, cinder, lapilli, tephra. GG
Expose Bolson

Bolson Technical Terms
Bolson: A term applied to an internally drained (closed) intermontane basin in arid regions where drainages from adjacent mountains converge toward a central depression. Bolsons are often tectonically formed depressions. According to Peterson, a bolson can include alluvial flat, alluvial plain, beach plain, barrier beach, lake plain, sand sheet, dune, and playa landforms. The piedmont slope above a bolson includes erosional (pediments) and older depositional surfaces (fans) that adjoin the mountain front. A semi-bolson is an externally drained (open) bolson. Synonym - intermontane basin. GG and FFP.
Discover Bar

Bar Technical Terms
Bar: A small, sinuous or arcuate, ridge-like lineation on a flood plain and separated from others by small channels or troughs; caused by fluvial processes and common to flood plains and young alluvial terraces; a constituent part of bar and channel topography. Compare – meander scroll. SW
Explain Barchan Dune

Barchan Dune Technical Terms
Barchan Dune: A crescent-shaped dune with tips extending leeward (downwind), making this side concave and the windward (upwind) side convex. Barchan dunes tend to be arranged in chains extending in the dominant wind direction. Compare - parabolic dune. HP
Expose Barrier Beach

Barrier Beach Technical Terms
Barrier Beach: (a) A narrow, elongate, coarse-textured, intertidal, sloping landform that is generally parallel with the beach ridge component of a barrier island or spit and adjacent to the ocean. Compare – barrier island. SSS (b) [relict] (colloquial: western U.S.A.) A wide, gently-sloping portion of a bolson floor comprising numerous, parallel, closely-spaced, relict longshore-bars and lagoons built by a receding pluvial lake. Synonym, offshore barrier, offshore beach, bar beach. Compare - bar [coast], barrier island. GG and FFP
Explain Barrier Flat

Barrier Flat Technical Terms
Barrier Flat: A relatively flat, low-lying area, commonly including pools of water, separating the exposed or seaward edge of a barrier beach or barrier island from the lagoon behind it. An assemblage of both deflation flats left behind migrating dunes and /or storm washover sediments; may be either barren or vegetated. Compare – barrier beach, back-barrier flat. SSS
Discover Barrier Island

Barrier Island Technical Terms
Barrier Island: A long, narrow, sandy island, that is above high tide and parallel to the shore that commonly has dunes, vegetated zones, and swampy or marshy terrains extending lagoonward from the beach. Compare – barrier beach.GG
Discover Basal Till
Basal Till Technical Terms
Basal Till: (a) (not preferred; obsolete) refer to subglacial till. Unconsolidated material of mixed composition deposited at the base (bottom) of a glacier [ The term emphasizes only the relative position of deposition; e.g. subglacial till]. Types of basal till include lodgment, melt-out, and flow till. GG & SW (b) [obsolete- use lodgment till] - A firm, dense, clay-rich till containing many abraded stones (coarse fragments) dragged along beneath a moving glacier and deposited upon bedrock or other glacial deposits. GG
Remember Base Slope

Base Slope Technical Terms
Base Slope: A geomorphic component of hills consisting of the concave to linear slope (perpendicular to the contour) which, regardless of the lateral shape is an area that forms an apron or wedge at the bottom of a hillside dominated by colluvial and slope wash processes and sediments (e.g., colluvium and slope alluvium). Distal base slope sediments commonly grade to, or interfinger with, alluvial fills, or gradually thin to form pedisediment over residuum. Compare - head slope, side slope, nose slope, interfluve, free face. SW
Expose Basin

Basin Technical Terms
Basin: (a) Drainage basin; (b) A low area in the Earth's crust, of tectonic origin, in which sediments have accumulated. GG (c) (colloquial: western USA) A general term for the nearly level to gently sloping, bottom surface of an intermontane basin (bolson). Landforms include playas, broad alluvial flats containing ephemeral drainageways, and relict alluvial and lacustrine surfaces that rarely, if ever, are subject to flooding. Where through-drainage systems are well developed, flood plains are dominant and lake plains are absent or of limited extent. Basin floors grade mountainward to distal parts of piedmont slopes. FFP
Discover Basin Floor
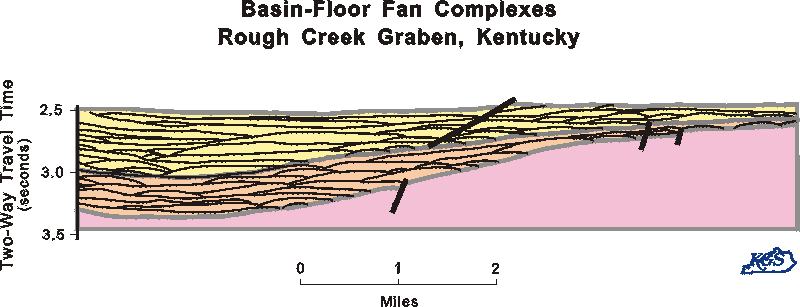
Basin Floor Technical Terms
Basin Floor: A general term for the nearly level, lower-most part of intermontane basins (i.e. bolsons, semi-bolsons). The floor includes all of the alluvial, eolian, and erosional landforms below the piedmont slope. Compare - basin, piedmont slope. FFP
Explain Basin-Floor Remnant

Basin-Floor Remnant Technical Terms
Basin-Floor Remnant: (colloquial: western U.S.A.) A relatively flat, erosional remnant of any former landform of a basin floor that has been dissected following the incision of an axial stream. FFP
Explain Batholiths

Batholiths Technical Terms
Batholiths: A large, generally discordant plutonic rock body exposed at the land surface, with an aerial extent > 40 sq. mi. (100 km2) and no known bottom (e.g. Idaho batholith). Compare – stock. SW & GG
Remember Bay

Bay Technical Terms
Bay: (a) Any terrestrial formation resembling a bay of the sea, as a recess or extension of lowland along a river valley or within a curve in a range of hills, or an arm of a prairie extending into, or partly surrounded by, a forest. (b) A Carolina Bay. GG & GSST.
Explain Bay Bottom

Bay Bottom Technical Terms
Bay Bottom: The nearly level or slightly undulating central portion of a submerged, low-energy, depositional estuarine embayment characterized by relatively deep water (1.0 to >2.5 m). Compare – lagoon bottom. SSS
Expose Bayou

Bayou Technical Terms
Bayou: A term applied to many local water features in the lower Mississippi River basin and in the Gulf Coast region of the U.S. Its general meaning is a creek or secondary watercourse that is tributary to another body of water; especially a sluggish and stagnant stream that follows a winding course through alluvial lowlands, coastal swamps or river deltas. Compare - oxbow, slough. GG
Discover Beach

Beach Technical Terms
Beach: (a) A gently sloping zone of unconsolidated material, typically with a slightly concave profile, extending landward from the low-water line to the place where there is a definite change in material or physiographic form (such as a cliff) or to the line of permanent vegetation (usually the effective limit of the highest storm waves); a shore of a body of water, formed and washed by waves or tides, usually covered by sand or gravel; (b) the relatively thick and temporary accumulation of loose water-borne material (usually well-sorted sand and pebbles) accompanied by mud, cobbles, boulders, and smoothed rock and shell fragments, that is in active transit along, or deposited on, the shore zone between the limits of low water and high water. GG
Remember Beach Plain
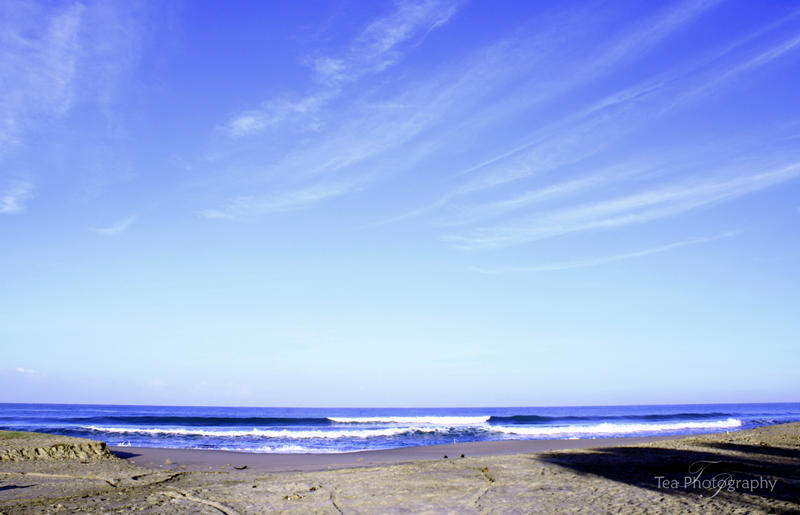

Beach Plain Technical Terms
Beach Plain: A continuous and level or undulating area formed by closely spaced successive embankments of wave-deposited beach material added more or less uniformly to a prograding shoreline, such as to a growing compound spit or to a cuspate foreland. Compare - wave-built terrace, chenier plain. GG
Remember Beach Ridge

Beach Ridge Technical Terms
Beach Ridge: A low, essentially continuous mound of beach or beach-and-dune material heaped up by the action of waves and currents on the backshore of a beach, beyond the present limit of storm waves or the reach of ordinary tides, and occurring singly or as one of a series of approximately parallel deposits. The ridges are roughly parallel to the shoreline and represent successive positions of an advancing shoreline. GG
Discover Beach Sands

Beach Sands Technical Terms
Beach Sands: Well sorted, sand-sized, clastic material transported and deposited primarily by wave action and deposited in a shore environment. Compare - eolian sands. SW
Remember Beach Terrace

Beach Terrace Technical Terms
Beach Terrace: (a) A landform that consists of a wave-cut scarp and wave-built terrace of well-sorted sand and gravel of marine and lacustrine origin. (b) (colloquial: western U.S.A.) relict shorelines from pluvial lakes, generally restricted to valley sides. Compare - strandline, shoreline. FFP
Explain Beaded Stream Pattern

Beaded Stream Pattern Technical Terms
Beaded Stream Pattern: A characteristic pattern of small streams in areas underlain by ice wedges. The course of the stream channel is controlled by the pattern of the wedges, with beads (pools) occurring at the junctions of the wedges. NRC
Discover Bed

Bed Technical Terms
Bed: The layer of sediments or sedimentary rocks bounded above and below by more or less well-defined bedding surfaces. The smallest, formal lithostratigraphic unit of sedimentary rocks. The designation of a bed or a unit of beds as a formally named lithostratigraphic unit generally should be limited to certain distinctive beds whose recognition is particularly useful. Coal beds, oil sands, and other layers of economic importance commonly are named, but such units and their names usually are not a part of formal stratigraphic nomenclature. Compare - formation. GG
Explain Bedded

Bedded Technical Terms
Bedded: Formed, arranged, or deposited in layers or beds, or made up of or occurring in the form of beds; especially said of a layered sedimentary rock, deposit, or formation. GG
Discover Bedding Plane
Bedding Plane Technical Terms
Bedding Plane: A planar or nearly planar bedding surface that visibly separates each successive layer of stratified sediment or rock (of the same or different lithology) from the preceding or following layer; a plane of deposition. It often marks a change in the circumstances of deposition, and may show a parting, a color difference, a change in particle size, or various combinations. A term commonly applied to any bedding surface even when conspicuously bent or deformed by folding. SW & GG
Expose Bedrock

Bedrock Technical Terms
Bedrock: A general term for the solid rock that underlies the soil and other unconsolidated material or that is exposed at the surface. Compare - regolith, residuum. GG
Remember Berm
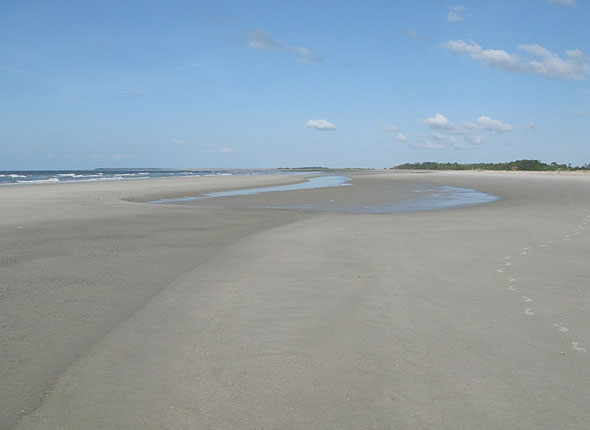

Berm Technical Terms
Berm: A low, impermanent, nearly horizontal or landward-sloping shelf, ledge, or narrow terrace on the backshore of a beach, formed of material thrown up and deposited by storm waves; it is generally bounded on one side or the other by a beach ridge or beach scarp. Some beaches have no berms, others have one or several. GG
Remember Beveled Base
Beveled Base Technical Terms
Beveled Base: The lower portion of a canyon wall or escarpment marked by a sharp reduction in slope gradient from the precipitous cliff above, and characteristically composed of thinly mantled colluvium (e.g. < 1 m) and / or carapaced with a thin surficial mantle of large rock fragments from above, which overly residuum of less resistant rock (e.g., shale) whose thin strata intermittently outcrop at the surface; a zone of erosion and transport common in the canyonlands of the semi-arid, southwestern USA. Compare – talus slope. SW
Explain Beveled Cut

Beveled Cut Technical Terms
Beveled Cut: A bank or slope portion of a cut excavated into unconsolidated material (regolith) or bedrock as in a roadcut, whose slope gradient has been mechanically reduced to a subdued angle (e.g. to < 33 %) to increase slope stability, reduce erosion, or to facilitate revegetation. Compare – cut, cutbank, roadcut. SW
Discover Blind Valley
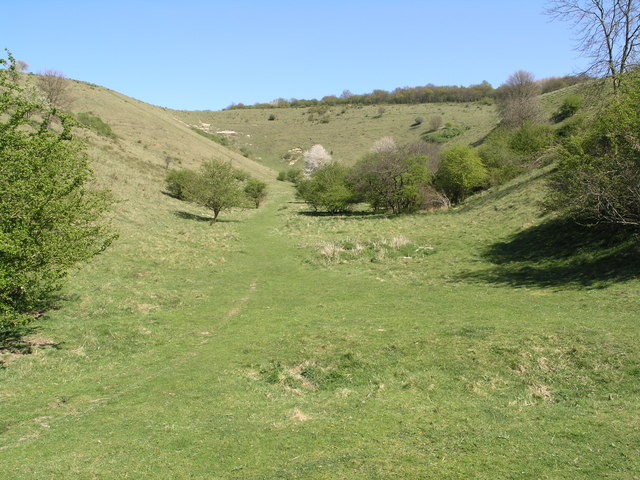

Blind Valley Technical Terms
Blind Valley: A valley, commonly in karst, that ends abruptly downstream at the point at which its stream disappears underground. GG
Remember Block

Block Technical Terms
Block: A pyroclast that was ejected in a solid state; it has a diameter greater than 64 mm. Compare - bomb, cinder, lapilli, tephra. GG
Expose Block Field

Block Field Technical Terms
Block Field: A thin accumulation of stone blocks, typically angular, with only coarse fragments in the upper part, over solid or weathered bedrock, colluvium, or alluvium, without a cliff or ledge above as an apparent source. Block fields occur on high mountain slopes above tree-line, or in polar or paleo-periglacial regions; they are most extensive along slopes parallel to the contour; and they generally occur on slopes of less than 5%. Synonym - felsenmeer. Compare - block stream, talus slope, scree slope. GG
Discover Bog

Bog Technical Terms
Bog: Waterlogged, spongy ground, consisting primarily of mosses, containing acidic, decaying vegetation such as sphagnum, sedges, and heaths that may develop into peat. Compare - fen, marsh, swamp. GG
Discover Bluff

Bluff Technical Terms
Bluff: (a) A high bank or bold headland, with a broad, precipitous, sometimes rounded cliff face overlooking a plain or body of water, especially on the outside of a stream meander; ex. a river bluff. (b) (not preferred) use cliff. Any cliff with a steep, broad face. GG
Discover Blue Rock
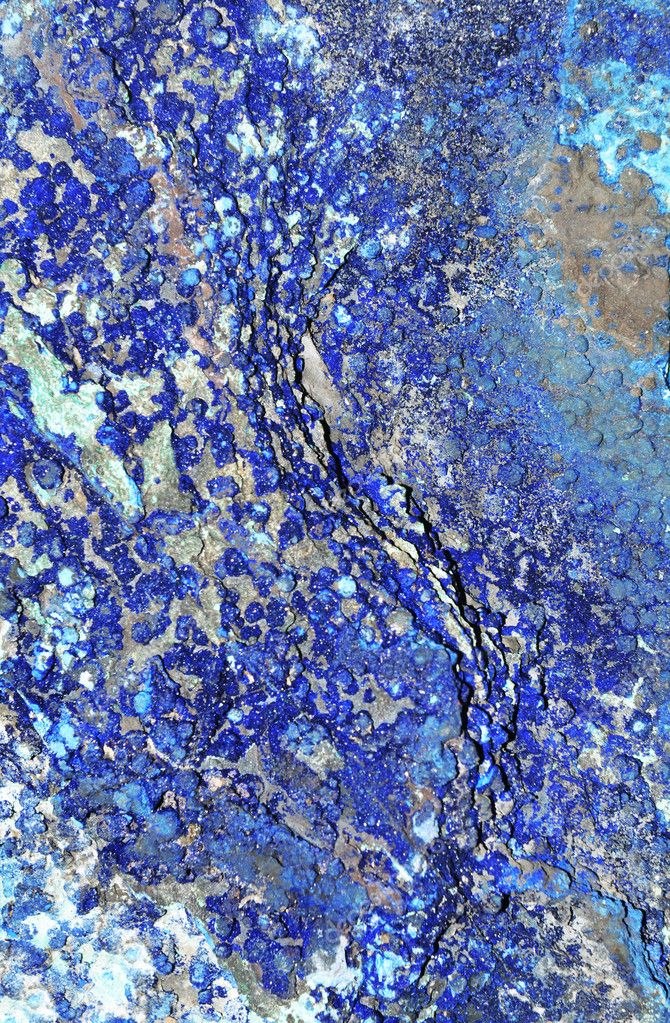
Blue Rock Technical Terms
Blue Rock: The very dense (e.g. 2.75 g/cc), extremely hard and massive, nominally vesicular lava that commonly forms the inner core of an `a`a lava flow. SW
Explain Blowout

Blowout Technical Terms
Blowout: A saucer-, cup-, or trough-shaped depression formed by wind erosion on a preexisting dune or other sand deposit, especially in an area of shifting sand, loose soil, or where protective vegetation is disturbed or destroyed; the adjoining accumulation of sand derived from the depression, where recognizable, is commonly included. Commonly small, some blowouts may be large (kilometers in diameter). Compare – deflation basin. GG
Remember block stream

block stream Technical Terms
block stream: An accumulation of boulders or angular blocks, with no fine sizes in the upper part, overlying solid or weathered bedrock, colluvium, or alluvium, and lying below a cliff or ledge from which coarse fragments originate. Block streams usually occur at the heads of ravines as narrow bodies that are more extensive downslope than along the slope. They may exist on any slope angle, but ordinarily not steeper than 90 percent slope (approx. 40 degrees). Compare - block field. GG
Expose block lava flow

block lava flow Technical Terms
block lava flow: A lava flow dominated by block lava. Compare –`a`a lava flow, pahoehoe lava flow, pillow lava flow. SW
Expose Block Lava
Block Lava Technical Terms
Block Lava: Lava having a surface of angular blocks; it is similar to `a`a lava but the fragments are larger and more regular in shape, somewhat smoother, and less vesicular. Compare – `a`a lava, pahoehoe lava, pillow lava. GG
Remember Block Glide

Block Glide Technical Terms
Block Glide: The process, associated sediments (block glide deposit) or resultant landform characterized by a slow type of slide, in which largely intact units (blocks) of rock or soil slide downslope along a relatively planar surface, such as a bedding plane, without any significant distortion of the original mass; a type of translational rock slide. Compare – rotational landslide, debris slide, lateral spread, landslide. SW & DV

