Remember Permafrost

Permafrost Technical Terms
Permafrost: Ground, soil, or rock that remains at or below 0o C for at least two years. It is defined on the basis of temperature and is not necessarily frozen. Compare - continuous permafrost, discontinuous permafrost, sporadic permafrost, thaw-stable permafrost, thaw sensitive permafrost. NRC
Discover Physiographic Division

Physiographic Division Technical Terms
Physiographic Division: A large portion of a continent of which all parts are similar in geologic structure and climate at a small scale (e.g. 1:5,000,000) and which has consequently had a unified geomorphic history and whose pattern of relief or landforms differ significantly from that of adjacent areas. Examples: the Laurentian Upland, Rocky Mountain System, and Interior Highlands of the U.S.A. western U.S.A. [The highest level in the Physiographic Location part of the Geomorphic Description System]. SW & NASIS Data Dictionary
Remember Physiographic Province
Physiographic Province Technical Terms
Physiographic Province: A region of which all parts are similar in geologic structure and climate and which has consequently had a unified geomorphic history; a region whose pattern of relief or landforms differ significantly from that of adjacent regions; i.e. a subset within a Physiographic Division. Examples: the Valley and Ridge, Blue Ridge, and Piedmont provinces in the eastern U.S.A., and the Basin and Range, Rocky Mountains, and Great Plains provinces in the western U.S.A. [The second highest level in the Physiographic Location part of the Geomorphic Description System]. SW & GG
Discover Physiographic Section

Physiographic Section Technical Terms
Physiographic Section: An area which all parts are similar in geologic structure and climate at a relatively small scale and which has consequently had a unified geomorphic history, and whose pattern of relief or landforms differ significantly from that of adjacent areas ( = Fenneman's (1957) "Section"); i.e. a subset within a Physiographic Province). Examples: the Mohawk, Green Mountain, and Floridian Sections in the eastern U.S.A. and the Sacramento Section, Puget Trough, and Klamath Mountains in the western U.S.A. [The third highest level in the Physiographic Location part of the Geomorphic Description System]. SW, NASIS Data Dictionary
Expose Piedmont

Piedmont Technical Terms
Piedmont : Lying or formed at the base of a mountain or mountain range; e.g., a piedmont terrace or a piedmont pediment. (noun) An area, plain, slope, glacier, or other feature at the base of a mountain; e.g., a foothill or a bajada. In the United States, the Piedmont (noun) is a low plateau extending from New Jersey to Alabama and lying east of the Appalachian Mountains. GG
Explain Piedmont Slope

Piedmont Slope Technical Terms
Piedmont Slope: The dominant gentle slope at the foot of a mountain; generally used in terms of intermontane-basin terrain in arid to subhumid regions. Main components include: (a) An erosional surface on bedrock adjacent to the receding mountain front (pediment, rock pediment); (b) A constructional surface comprising individual alluvial fans and interfan valleys, also near the mountain front; and (c) A distal complex of coalescent fans (bajada), and alluvial slopes without fan form. Piedmont slopes grade to basin-floor depressions with alluvial and temporary lake plains or to surfaces associated with through drainage (e.g., axial streams). Compare – bolson, fan piedmont. HP
Discover Pillow Lava
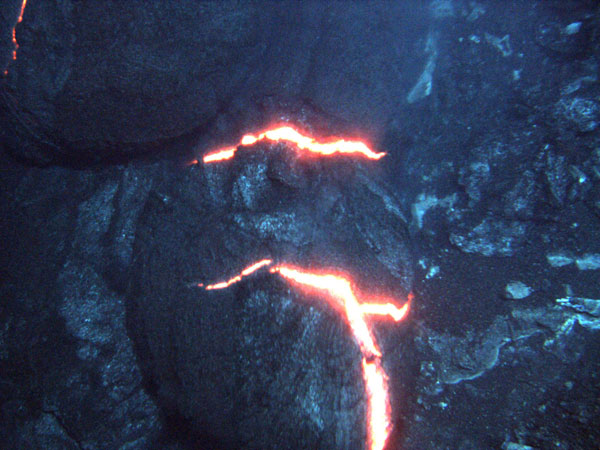

Pillow Lava Technical Terms
Pillow Lava: A general term for lava displaying pillow structure (discontinuous, close-fitting, bun-shaped or ellipsoidal masses, generally < 1 m in diameter); considered to have formed in a subaqueous environment; such lava is usually basaltic or andesitic. Compare – `a`a lava, block lava, pahoehoe lava. SW, GG, & GS
Remember Pillow Lava Flow

Pillow Lava Flow Technical Terms
Pillow Lava Flow: A lava flow or body displaying pillow structure and considered to have formed in a subaqueous environment (underwater); usually basaltic or andesitic in composition. Compare –`a`a lava flow, block lava flow, pahoehoe lava flow. SW & GS
Expose Pimple Mound

Pimple Mound Technical Terms
Pimple Mound: Low, flattened, approximately circular or elliptical features composed of sandy loam that is coarser than, and distinct from, the surrounding soil; the basal diameter ranges from 3 m to more than 30 m, and the height from 30 cm to more than 2 m. Compare - mima mound, patterned ground, shrub-coppice dune. GG
Remember Pingo

Pingo Technical Terms
Pingo: A large frost mound; especially a relatively large conical mound of soil-covered ice (commonly 30 to 50 meters high and up to 400 meters in diameter) raised in part by hydrostatic pressure within and below the permafrost of Arctic regions, and of more than 1 year's duration. GG
Discover Pinnacle

Pinnacle Technical Terms
Pinnacle: A tall, slender, tapering tower or spire-shaped pillar of rock, either isolated, as on steep slopes or cliffs formed in karst or other massive rocks, or at the summit of a hill or mountain. Compare - erosional remnant, hoodoo. SW, GG, & WW
Explain Pinnate Drainage Pattern

Pinnate Drainage Pattern Technical Terms
Pinnate Drainage Pattern: A variation of the dendritic drainage pattern in which the main stream receives many closely spaced, subparallel tributaries that join it at slightly acute angles upstream, resembling in plan a feather. They typically form on steep slopes with soils that have a high silt content; such as loess landscapes or fine-textured flood plains. SW, GG, WA
Discover Pitted Outwash

Pitted Outwash Technical Terms
Pitted Outwash: Outwash deposits with surficial pits or kettles, produced by the partial or complete burial of glacial ice by outwash and the subsequent thaw of the ice and collapse of the surficial materials. Compare - pitted outwash plain. GG
Remember Pitted Outwash Plain

Pitted Outwash Plain Technical Terms
Pitted Outwash Plain: An outwash plain marked by many irregular depressions such as kettles, shallow pits, and potholes which formed by melting of incorporated ice masses; much of the gradient and internal structures of the original plain remain intact; many are found in WI, MN, MI, and IN. Compare – collapsed outwash plain, outwash, pitted outwash. GG
Discover Pitted Outwash Terrace

Pitted Outwash Terrace Technical Terms
Pitted Outwash Terrace: A relict glaciofluvial terrace that retains its original attitude, composed of undistorted outwash sediments and depositional structures and whose surface is pock-marked with numerous potholes or kettle depressions. Compare – collapsed outwash plain. SW
Explain Plain

Plain Technical Terms
Plain: A general term referring to any flat, lowland area, large or small, at a low elevation. Specifically, any extensive region of comparatively smooth and level gently undulating land. A plain has few or no prominent hills or valleys but sometimes has considerable slope, and usually occurs at low elevation relative to surrounding areas. Where dissected, remnants of a plain can form the local uplands. A plain may be forested or bare of trees and may be formed by deposition or erosion. Compare - lowland, plateau. GG
Expose Plateau

Plateau Technical Terms
Plateau: A comparatively flat area of great extent and elevation; specifically an extensive land region considerably elevated (more than 100 meters) above adjacent lower-lying terrain, and is commonly limited on at least one side by an abrupt descent, has a flat or nearly level surface. A comparatively large part of a plateau surface is near summit level. Compare - hill, foothill, mountain, mesa, plain. GG
Remember Playa

Playa Technical Terms
Playa: The usually dry and nearly level lake plain that occupies the lowest parts of closed depressions, such as those occurring on intermontane basin floors. Temporary flooding occurs primarily in response to precipitation-runoff events. Playa deposits are fine grained and may or may not have high water table and saline conditions. HP
Discover Playa Dune

Playa Dune Technical Terms
Playa Dune: A linear or curvilinear ridge of windblown, granular material (generally sand or parna) removed from the adjacent basin by wind erosion (deflation), and deposited on the leeward (prevailing downwind) margin of a playa, playa basin, or salina basin. The dune may be barren or vegetated. Compare – dune. SW
Discover Playa Floor

Playa Floor Technical Terms
Playa Floor: The lowest extensive, flat to slightly concave surface within a playa basin, consisting of a dry lake bed or lake plain underlain by stratified clay, silt or sand, and commonly by soluble salts. Compare – playa step. SW
Discover Playa Lake

Playa Lake Technical Terms
Playa Lake: A shallow, intermittent lake in a arid or semi-arid region, covering or occupying a playa in the wet season but drying up in summer; an ephemeral lake that upon evaporation leaves or forms a playa. GG
Remember Playa Rim

Playa Rim Technical Terms
Playa Rim: The convex, upper margin (shoulder) of a playa basin where the playa slope intersects the surrounding terrain. Compare – playa slope. SW
Discover Playa Slope

Playa Slope Technical Terms
Playa Slope: The generally concave to slightly convex area within a playa basin that lies between the relatively level playa floor below (or playa step, if present) and the convex playa rim above. Overland flow is typically parallel down slope. Compare – playa step, playa rim. SW
Expose Playa Step
Playa Step Technical Terms
Playa Step: The relatively level or gently inclined “terrace-like” bench or toeslope within a large playa basin flanking and topographically higher than the playa floor and below the playa slope; a bench or step-like surface within a playa basin that breaks the continuity of the playa slope and modified by erosion and/or deposition. Temporary ponding may occur in response to precipitation / runoff events. Compare – playa slope. SW
Expose Playette

Playette Technical Terms
Playette: A very small, playa-like, shallow, closed depression typically with a salt-encrusted surface, little or no vegetation in semi-arid to arid climates and infrequently subject to ponding from precipitation events; commonly lacks the component parts of a playa except for a small playa floor. Compare – playa. SW & GHG
Explain Pleistocene

Pleistocene Technical Terms
Pleistocene: The epoch of the Quaternary Period of geologic time (from about 10 to 12 thousand to 1.6 million years ago), following the Pliocene Epoch and preceding the Holocene also the corresponding (time-stratigraphic) "series" of earth materials. SW & HP
Remember Pliocene

Pliocene Technical Terms
Pliocene: The last epoch (from 1.6 to 5.2 million years ago) of the Tertiary Period of geologic time that follows the Miocene and precedes the Pleistocene Epoch; also, the corresponding (time-stratigraphic) "series" of earth materials. HP
Expose Plug

Plug Technical Terms
Plug: A consolidated crater-filling of lava, the surrounding material of which has been largely removed by erosion leaving an isolated hill or knob. Compare – neck [volcanic]. SW & GG
Discover Plutonic

Plutonic Technical Terms
Plutonic: Pertaining to igneous rocks formed at great depth, but also including associated metamorphic rocks. GG
Remember Pluvial Lake

Pluvial Lake Technical Terms
Pluvial Lake: A lake formed in a period of exceptionally heavy rainfall; a lake formed in the Pleistocene Epoch during a time of glacial advance, and now either extinct (relict) or existing as a remnant (lake); e.g., Lake Bonneville. Compare - glacial lake, proglacial lake. GG
Remember Pocosin

Pocosin Technical Terms
Pocosin: A large wet area on broad, commonly a swamp, which occurs on nearly level interfluves in the Atlantic coastal plain with distinctive, native vegetation relative to adjacent areas. Soils may be either mineral or organic. A Native American term for "swamp on a hill." Compare - raised bog. RD
Remember Point Bar

Point Bar Technical Terms
Point Bar: Low, arcuate, subaerial ridges of sand developed adjacent to an inlet and formed by the lateral accretion or movement of the channel. Compare – sit. SSS
Discover Polygon

Polygon Technical Terms
Polygon: A type of patterned ground consisting of a closed, roughly equidimensional figure bounded by more or less straight sides; some sides may be irregular. Refer to patterned ground. Compare - High center polygon, low center polygon, ice wedge polygon, nonsorted polygon. NRC
Expose Pond

Pond Technical Terms
Pond: (a) A natural body of standing fresh water occupying a small surface depression, usually smaller than a lake and larger than a pool. (b) A small artificial body of water, used as a source of water. Compare - salt pond. GG
Explain Pool
Pool Technical Terms
Pool: A small, natural body of standing water, usually fresh; e.g. a stagnant body of water in a marsh, or a transient puddle in a depression following a rain. GG
Remember Porcellanite

Porcellanite Technical Terms
Porcellanite: A dense, siliceous rock formed as a indurated or baked clay or shale with a dull, light-colored, cherty appearance, often found in the roof or floor of a burned-out coal seam. GG
Expose Pothole
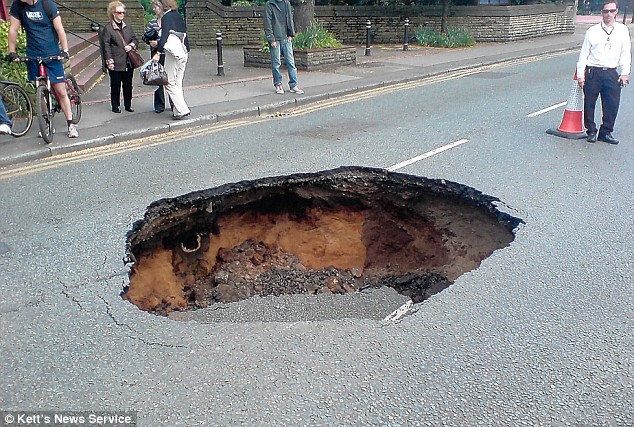

Pothole Technical Terms
Pothole : A type of small pit or closed depression (1 to 15 meters deep), generally circular or elliptical, occurring in an outwash plain, a recessional moraine, or a till plain. GG
Discover pothole
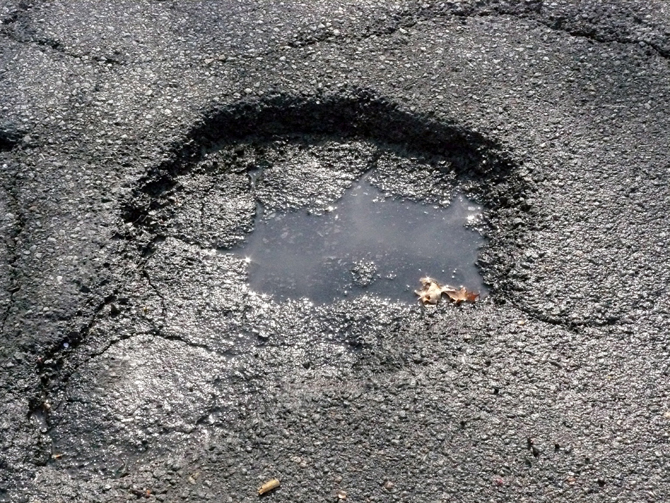

pothole Technical Terms
pothole: A shallow depression, generally less than 10 hectares in area, occurring on disintegration moraines and commonly containing an intermittent or seasonal pond or marsh. GG
Discover Pressure Ridge

Pressure Ridge Technical Terms
Pressure Ridge: An elongate uplift of the congealing crust of a lava flow, probably due to the pressure of the underlying, still-flowing lava; commonly < 5 m in height (but range up to 15 m) and < 100 m length (but can exceed 500 m). Compare – tumulus. SW, GG, & GS
Explain Proglacial Lake
Proglacial Lake Technical Terms
Proglacial Lake: Remnant features of a glacial lake that is now extinct which formed just beyond the margin of an advancing or retreating glacier; generally in direct contact with the ice. Compare - proglacial lake, pluvial lake. SW
Remember Proximal
Proximal Technical Terms
Proximal: Said of a sedimentary deposit consisting of coarse clastics and deposited nearest the source area. Compare - distal. GG
Discover Puff

Puff Technical Terms
Puff: A surface drape or exposure of up-welled substratum material forced to the surface and outcropping on a low mound or rim; the surface exposure of a chimney [gilgai]; a type of diapir composed of earthy material. Compare – chimney, intermediate position [gilgai], gilgai. SW
Explain Pumice

Pumice Technical Terms
Pumice: Rock fragments > 2 mm in diameter (i.e., retained upon a 2 mm sieve), or coherent rock layers (pumice flow), made of light-colored, vesicular, glassy rock commonly having the composition of rhyolite. The material commonly has a specific gravity of < 1.0 and is thereby sufficiently buoyant to float on water. SW; pumice-like fragments < 2 mm in size are called pumiceous ash. ST; Compare - scoria, tephra; (b) [geology] same as (a) but does not include any size restrictions. SW.
Expose Pyroclastic
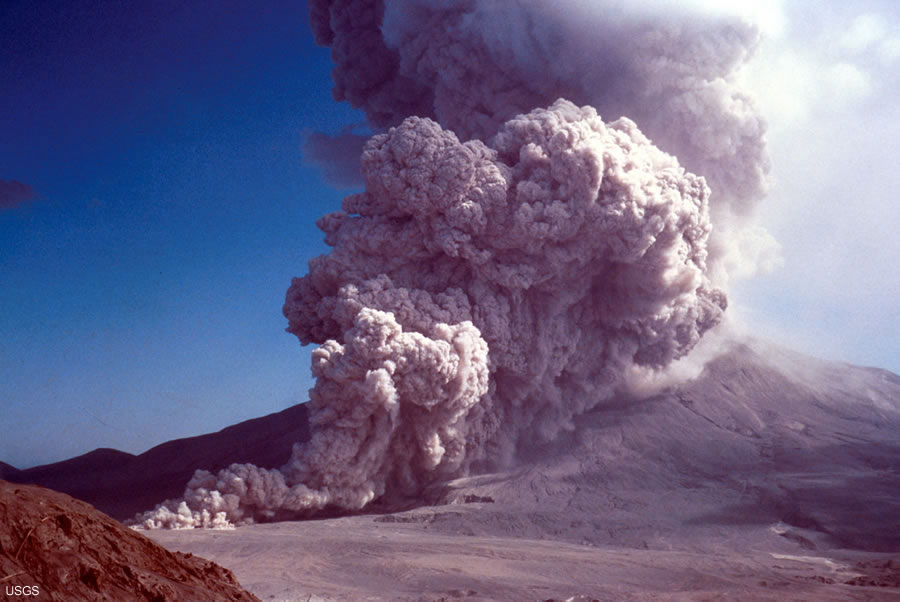

Pyroclastic Technical Terms
Pyroclastic: Pertaining to clastic rock particles produced by explosive, aerial ejection from a volcanic vent. Such materials may accumulate on land or under water. Compare - epiclastic, volcaniclastic, clastic. G. Smith & HP
Explain Pyroclastic Flow

Pyroclastic Flow Technical Terms
Pyroclastic Flow: A fast density current of pyroclastic material, usually very hot, composed of a mixture of gasses and a variety of pyroclastic particles (ash, pumice, scoria, lava fragments, etc.); produced by the explosive disintegration of viscous lava in a volcanic crater or by the explosive emission of gas-charged ash from a fissure and which tends to follow topographic lows (e.g. valleys) as it moves; used in a more general sense than ash flow. Compare –pyroclastic surge, ash flow, nueé ardente, lahar. SW, SN, GG
Remember Pyroclastic Surge

Pyroclastic Surge Technical Terms
Pyroclastic Surge: A low density, dilute, turbulent pyroclastic flow, usually very hot, composed of a generally unsorted mixture of gases, ash, pumice and dense rock fragments that travels across the ground at high speed and less constrained by topography than a pyroclastic flow; several types of pyroclastic surges can be specified (e.g. base surge, ash-cloud-surge). Compare - pyroclastic flow. SW, SN, GG
Expose Quaternary

Quaternary Technical Terms
Quaternary: The period of the Cenozoic Era of geologic time, extending from the end of the Tertiary Period (about 1.6 million years ago) to the present and comprising two epochs, the Pleistocene (Ice Age) and Holocene (Recent); also, the corresponding (time-stratigraphic) "series" of earth materials. GG
Expose Radial Drainage Pattern
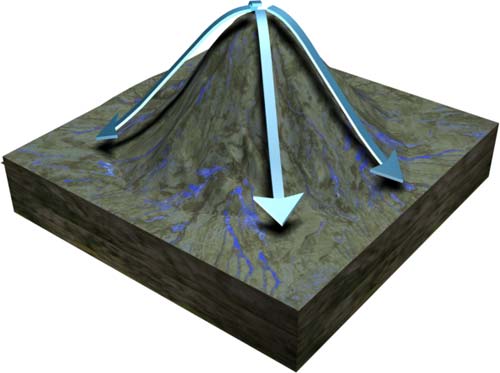
Radial Drainage Pattern Technical Terms
Radial Drainage Pattern: A drainage pattern in which consequent streams radiate or diverge outward, like the spokes of a wheel from a high central area.; a major collector stream is usually found in a curvilinear alignment around the bottom of the elevated topographic feature. It is best developed on the slopes of a young domal structure, a volcanic cone, or isolated hills (erosional remnant). SW, GG, WA
Remember Railroad Bed

Railroad Bed Technical Terms
Railroad Bed: The trace or track of a railroad route, commonly constructed slightly above the adjacent land, and composed mostly of earthy materials (gravel, rock fragments, etc.). Abandoned or reclaimed beds may no longer be topographically or visually distinct, but the materials used to construct them may still be a significant portion of the soil zone. SW
Expose Raised Beach

Raised Beach Technical Terms
Raised Beach: An ancient (relict) beach occurring above the present shoreline and separated from the present beach, having been elevated above the high-water mark either by local crustal movements (uplift) or by lowering of sea or lake level, and which may be bounded by inland cliffs. GG

