Explain Underfit Stream

Underfit Stream Technical Terms
Underfit Stream: A stream that appears to be too small to have eroded the valley in which it flows; a stream whose volume is greatly reduced or whose meanders show a pronounced shrinkage in radius. It is a common result of drainage changes effected by capture, glaciers, or climatic variations. GG
Remember Upland

Upland Technical Terms
Upland: An informal, general term for (a) the higher ground of a region, in contrast with a low-lying, adjacent land such as a valley or plain. (b) Land at a higher elevation than the flood plain or low stream terrace; land above the footslope zone of the hillslope continuum. Compare - lowland. HP & GG
Explain Uplift
Uplift Technical Terms
Uplift: A structurally high area in the earth's crust, produced by positive movements that raise or upthrust the rocks, as in a dome or arch. GG
Expose Upthrust

Upthrust Technical Terms
Upthrust: An upheaval of rock; said preferably of a violent upheaval. (b) A high angle gravity or thrust fault in which the relatively upthrown side was the active (moving) element. HP
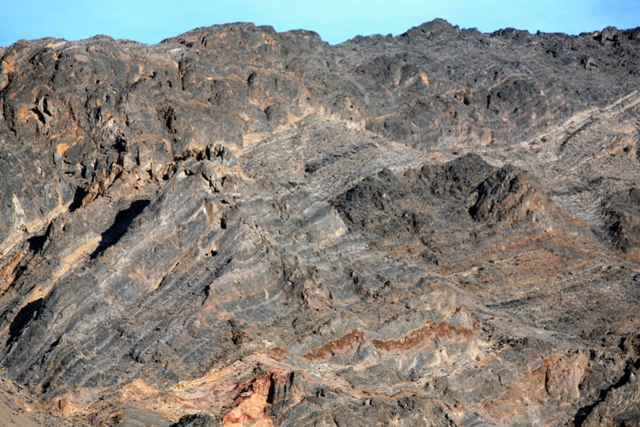
Expose U-Shaped Valley

U-Shaped Valley Technical Terms
U-Shaped Valley: A valley having a pronounced parabolic cross profile suggesting the form of a broad letter "U", with steep walls and a broad, nearly flat floor; specifically a valley carved by glacial erosion. Compare - V-shaped valley. GG
Remember Valley

Valley Technical Terms
Valley: An elongate, relatively large, externally drained depression of the Earth's surface that is primarily developed by stream erosion or glacial activity. Compare - basin. HP
Remember Valley-Border Surfaces

Valley-Border Surfaces Technical Terms
Valley-Border Surfaces: A general grouping of valley-side geomorphic surfaces of relatively large extent that occur in a stepped sequence graded to successively lower stream base levels, produced by episodic valley entrenchment; for example, multiple stream terrace levels, each with assemblages of constituent landforms (e.g. interfluves, hillslopes, fans, etc.) that dominate the margins of large river valleys. SW & HP
Expose Valley Fill

Valley Fill Technical Terms
Valley Fill: The unconsolidated sediment deposited by any agent (water, wind, ice, mass wasting) so as to fill or partly fill a valley. HP
Discover Valley Flat

Valley Flat Technical Terms
Valley Flat: A generic term for the low or relatively level ground lying between valley walls and bordering a stream channel; especially the small plain at the bottom of a narrow, steep-sided valley. The term can be generally applied noncommittally to a flat surface that cannot be identified with certainty as a floodplain or terrace. Compare – backswamp, meander belt. GG
Discover Valley Floor

Valley Floor Technical Terms
Valley Floor: A general term for the nearly level to gently sloping, lowest surface of a valley. Landforms include axial stream channels, the flood plain, flood-plain steps, and, in some areas, low terrace surfaces. Compare - flood-plain landforms, meander, braided channel, valley side. HP
Remember Valley Floor Remnant
-USA(July)/9)Gods,MokiDug+Bridges(UT)/images/za)%20And%20Cliffs%20Standing%20Above%20The%20Level%20Valley%20Floor,%20Remnants%20of%20Some%20Ancient%20Landscape%20....JPG)
Valley Floor Remnant Technical Terms
Valley Floor Remnant: Hills that are now erosion remnants of a former valley or basin floor, composed mostly of unconsolidated valley / basin fill sediments (e.g. alluvium) and typically lie well above the modern valley floor and flood plain. Former basin floor surfaces have become dissected and irregular and consist of hillslope positions (shoulder, backslope, etc.) and hill components (interfluve, headslope, etc.); common in large valleys of the western US. SW
Expose Valley Side

Valley Side Technical Terms
Valley Side: The sloping to very steep surfaces between the valley floor and summits of adjacent uplands. Well-defined, steep valley sides have been termed valley walls (not recommended). Note: Scale, relief, and perspective may require use of closely related terms such as hill slope or mountain slope. HP
Remember Valley Train

Valley Train Technical Terms
Valley Train: A long narrow body of outwash confined within a valley beyond a glacier; it may, or may not, emerge from the valley and join an outwash plain. GG
Explain Varve

Varve Technical Terms
Varve: A sedimentary layer, lamina, or sequence of laminae, deposited in a body of still water within 1 year; specifically, a thin pair of graded glaciolacustrine layers seasonally deposited, usually by meltwater streams, in a glacial lake or other body of still water in front of a glacier. Compare - rhythmite. GG
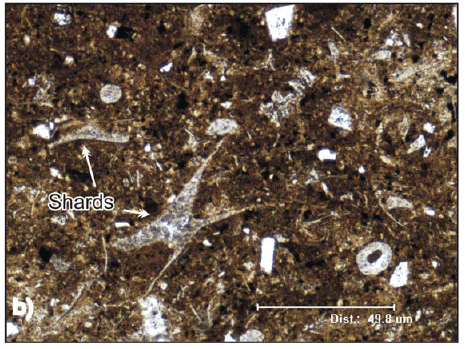
Discover Ventifact
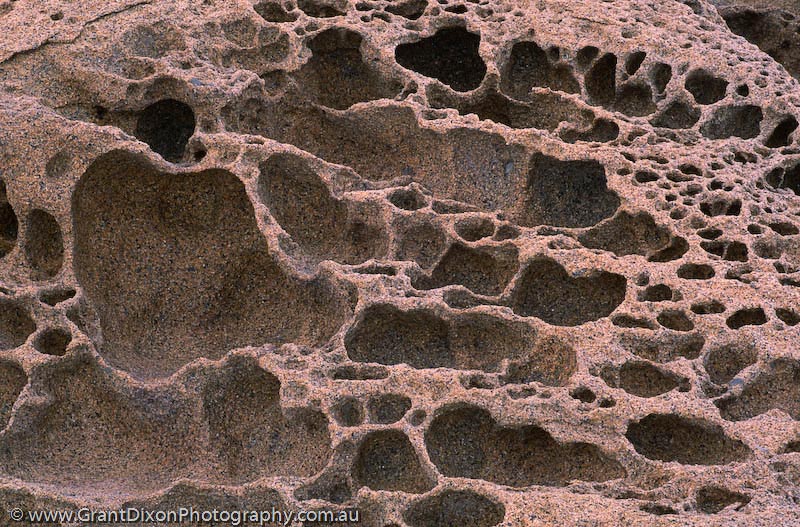
Ventifact Technical Terms
Ventifact: A stone or pebble that has been shaped, worn, faceted, cut, or polished by the abrasive action of windblown sand, usually under arid conditions. When the pebble is at the ground surface, as in a desert pavement, the upper part is polished while the lower or below ground part is angular or subangular. GG & HP
Remember Vernal Pool

Vernal Pool Technical Terms
Vernal Pool: A natural, seasonal pond in a small closed depression (micro-low) which supports a semi-aquatic or aquatic ecosystem adapted to annual cycles of standing water in the springtime followed by drying in the summer / autumn; commonly recognized in CA. SW
Explain Volcanic

Volcanic Technical Terms
Volcanic: Pertaining to (a) the deep seated (igneous) processes by which magma and associated gases rise through the crust and are extruded onto the earth's surface and into the atmosphere, and (b) The structures, rocks, and landforms produced. Compare - extrusive, volcaniclastic. HP
Discover Volcanic Breccia

Volcanic Breccia Technical Terms
Volcanic Breccia: A volcaniclastic rock composed mostly of angular rock fragments greater than 2 mm in size. The name volcanic breccia is not synonymous with pyroclastic breccia (volcanic breccia forms in different ways). GG
Explain Volcanic Cone

Volcanic Cone Technical Terms
Volcanic Cone: A conical hill of lava and/or pyroclastics that is built up around a volcanic vent. GG
Discover Volcanic Dome
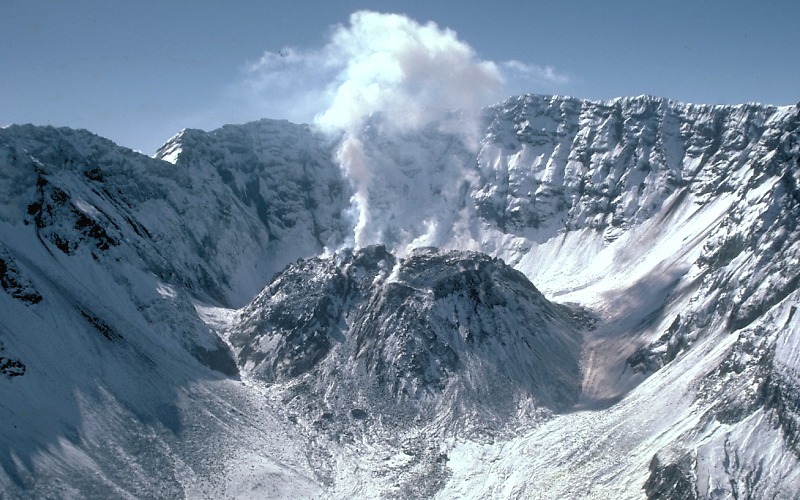

Volcanic Dome Technical Terms
Volcanic Dome: A steep-sided, rounded extrusion of highly viscous lava squeezed out from a volcano, and forming a dome-shaped or bulbous mass of congealed lava above and around the volcanic vent. GG
Remember Volcanic Field

Volcanic Field Technical Terms
Volcanic Field: A more or less well defined area that is covered with volcanic rocks of much more diverse lithology and distribution than a lava field, or that is so modified by age and erosion that it’s original topographic configuration, composition and extent is uncertain. Compare – lava field, lava plain. SW
Discover Volcaniclastic

Volcaniclastic Technical Terms
Volcaniclastic : Pertaining to the entire spectrum of fragmental materials with a preponderance of clasts of volcanic origin. The term includes not only pyroclastic materials but also epiclastic deposits derived from volcanic source areas by normal processes of mass movement and stream erosion. Examples: welded tuff, volcanic breccia. HP
Remember volcano

volcano Technical Terms
volcano: A vent in the surface of the Earth through which magma and associated gases and ash erupt; also, the form or structure, usually conical, that is produced by the ejected material. (b) Any eruption of material, e.g. mud, sand, etc. that resembles a magmatic volcano. GG
Discover V-shaped valley

V-shaped valley Technical Terms
V-shaped valley : A valley having a pronounced cross profile suggesting the form of the letter "V", characterized by steep sides and short tributaries; specifically a narrow valley resulting from downcutting by a stream. The "V" becomes broader as the downcutting progresses. Compare - U-shaped valley.GG
Expose Wash

Wash Technical Terms
Wash : The broad, flat-floored channel of an ephemeral stream, commonly with very steep to vertical banks cut in alluvium. Note: When channels reach intersect zones of ground-water discharge they are more properly classed as "intermittent stream" channels. Synonym - arroyo. Compare - gully. HP
Explain Washover Fan

Washover Fan Technical Terms
Washover Fan : fan-like deposit of sand washed over a barrier island or spit during a storm and deposited on the landward side. Washover fans can be small to medium sized and completely subaerial, or they can be quite large and include subaqueous margins extending into adjacent lagoons or estuaries. Large fans can be subdivided into sequential parts: ephemeral washover channel (microfeature) cut through dunes or beach ridges, back-barrier flats, (subaqueous) washover-fan flat, (subaqueous) washover-fan slope. Subaerial portions can range from barren to completely vegetated.. SSS
Explain Washover-Fan Flat
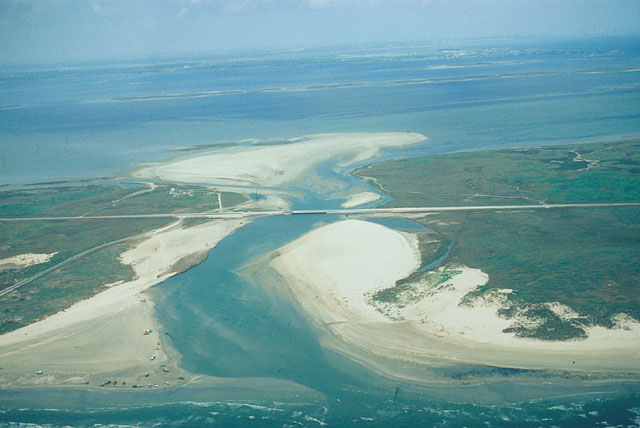

Washover-Fan Flat Technical Terms
Washover-Fan Flat : A gently sloping, fan-like, subaqueous landform created by overwash from storm surges that transports sediment from the seaward side to the landward side of a barrier island (GG). Sediment is carried through temporary overwash channels that cut through the dune complex on the barrier spit (Fisher and Simpson, 1979; Boothroyd et al., 1985; Davis, 1994) and spill out onto the lagoon-side platform where they coalesce to form a broad belt. Also called storm-surge platform flat (Boothroyd et al., 1985) and washover fan apron (GG). Compare – washover fan slope. SSS
Expose Washover-Fan Slope

Washover-Fan Slope Technical Terms
Washover-Fan Slope: A subaqueous extension of a washover-fan flat that slopes toward deeper water of a lagoon or estuary and away from the washover-fan flat. Compare – washover-fan flat. SSS
Explain Water

Water Technical Terms
Water : A generic map unit for any permanent, open body of water (pond, lake, reservoir, etc.) that does not support rooted plants. SW
Discover Waterway
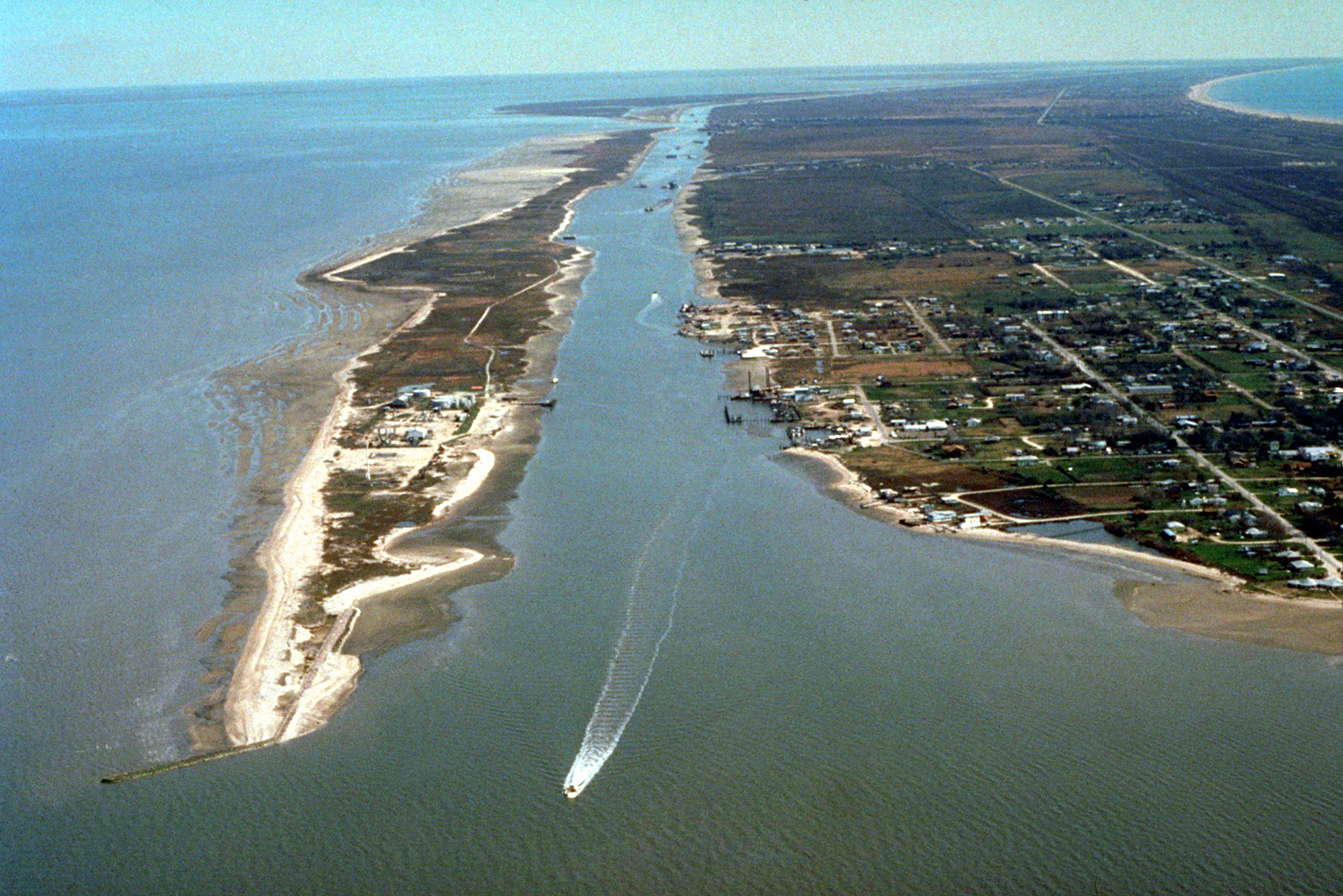

Waterway Technical Terms
Waterway : A general term for a way or channel, either natural (as a river) or artificial (as a canal), for conducting the flow of water. (b) A navigable body or stretch of water available for passage; a watercourse. Compare - drainageway. GG
Explain Wave-Built Terrace

Wave-Built Terrace Technical Terms
Wave-Built Terrace : A gently sloping coastal feature at the seaward or lakeward edge of a wave-cut platform, constructed by sediment brought by rivers or drifted along the shore or across the platform and deposited in the deeper water beyond. Compare – submerged wave-built terrace, beach plain, strand plain. GG
Explain Weathering

Weathering Technical Terms
Weathering : All physical disintegration, chemical decomposition, and biologically induced changes in rocks or other deposits at or near the earth's surface by atmospheric or biologic agents or circulating surface waters with essentially no transport of the altered material. These changes result in disintegration and decomposition of the material. Compare - regolith, residuum, saprolite. HP
Expose Wave-Cut Platform

Wave-Cut Platform Technical Terms
Wave-Cut Platform : A gently sloping surface produced by wave erosion, extending into the sea or lake from the base of the wave-cut cliff. This feature represents both the wave-cut bench and the abrasion platform. Compare – submerged wave-cut platform. GG
Remember Welding

Welding Technical Terms
Welding : Consolidation of sediments (especially of clays) by pressure resulting from the weight of superincumbent material or from earth movement, characterized by cohering particles brought within the limits of mutual molecular attraction as water is squeezed out of the sediments. (b) the diagenetic process whereby discrete crystals and/or grains become attached to each other during compaction, often involving pressure solution and pressure transfer. GG
Expose Wind Gap

Wind Gap Technical Terms
Wind Gap : A former water gap now abandoned by the stream that formed it, suggesting stream piracy or stream diversion. HP
Explain Wind-Tidal Flat

Wind-Tidal Flat Technical Terms
Wind-Tidal Flat : A broad, low-lying, nearly-level sand flat that is alternately inundated by ponded rainwater or by wind-driven bay or estuarine water from storm surges or seiche. Frequent salinity fluctuations and prolonged periods of subaerial exposure preclude establishment of most types of vegetation except for mats of filamentous blue-green algae. Compare – tidal flat. SSS & HF
Expose Window

Window Technical Terms
Window : An eroded area of a thrust sheet, commonly a basin or valley floor, that exposes the incongruous bedrock stratigraphy beneath the thrust-sheet; a particular structural or stratigraphic relationship is implied, rather than a particular topographic form. Common in the Appalachian and Rocky Mountain margins. Synonym: fenster. GG, WT, SW
Remember Woody Peat
Woody Peat Technical Terms
Woody Peat : An accumulation of organic material that is predominantly composed of trees, shrubs, and other woody plants. Compare herbaceous peat, moss peat, sedimentary peat, peat, muck, and mucky peat. SSM
Remember Yardang

Yardang Technical Terms
Yardang : A microfeature in the form of a long, irregular, sharp-crested, undercut ridge between two round-bottomed troughs, carved on a plateau or unsheltered plain in a desert region by wind erosion, and cut into soft but coherent deposits (such as clayey sand); it lies in the direction of the dominant wind, and may be up to 6 m high and 40 m wide. (b) A landform produced in a region of limestone or sandstone by infrequent rains combined with wind action, and characterized by “a surface bristling with a fine lacework of sharp ridges pitted by corrosion”. Compare – pavement karst. GG
Expose Yardang Trough

Yardang Trough Technical Terms
Yardang Trough : A long, shallow, round-bottomed groove, furrow, trough, or corridor excavated in the desert floor by wind abrasion, and separating two yardangs. Compare – yardang. GG
Explain Zibar

Zibar Technical Terms
Zibar : A small, low-relief sand dune that lacks discernible slip faces and commonly occurs on sand sheets, in interdune areas, or in corridors between larger dunes. Zibar spacing can range from 50 – 400 m with local relief < 10 m. Unlike coppice dunes, zibars are not related to deposition around vegetation. Generally dominated by coarser sands. Compare – dune, coppice dune. SW, GG, NL, CW.
Explain Barrier Cove

Barrier Cove Technical Terms
Barrier Cove: A subaqueous area adjacent to a barrier island or submerged barrier beach that forms a minor embayment or cove within the larger basin. Compare – cove, mainland cove. SSS
Expose Ballena

Ballena Technical Terms
Ballena : A fan remnant having a distinctively-rounded surface of fan alluvium. The ballena's broadly-rounded shoulders meet from either side to form a narrow summit and merge smoothly with concave side slopes and then concave, short pediments which form smoothly-rounded drainageways between adjacent ballenas. A partial ballena is a fan remnant large enough to retain some relict fan surface on a remnant summit. Compare - fan remnant. SW & FFP.
Discover Bald

Bald Technical Terms
Bald : An ecological term for the grass or shrub covered (naturally tree-less) summit of a high elevation hill or mountain, flanked by forested slopes; not above the local tree-line. Compare – glade. SW & GG
Expose Bajada

Bajada Technical Terms
Bajada: A broad, gently inclined, alluvial piedmont slope extending from the base of a mountain range out into a basin and formed by the lateral coalescence of a series of alluvial fans. Typically it has a broadly undulating transverse profile, parallel to the mountain front, resulting from the convexities of component fans. The term is generally restricted to constructional slopes of intermontane basins. Synonym - coalescent fan piedmont. Compare - fan apron. HP & SW
Discover Backswamp Deposit

Backswamp Deposit Technical Terms
Backswamp Deposit : Laminated of silt and clay deposited in the flood basin between valley sides or terraces and the natural levees of a river. Compare - slackwater. GG
Explain Backshore

Backshore Technical Terms
Backshore : The upper or inner, usually dry, zone of the shore or beach, lying between the high-water line of mean spring tides and the upper limit of shore-zone processes; it is acted upon by waves or covered by water only during exceptionally severe storms or unusually high tides. It is essentially horizontal or slopes gently landward, and is divided from the foreshore by the crest of the most seaward berm. Compare - washover fan. GG
Explain Backswamp

Backswamp Technical Terms
Backswamp : A flood-plain landform. Extensive, marshy or swampy, depressed areas of flood plains between natural levees and valley sides or terraces. Compare - valley flat. HP
Expose Backslope

Backslope Technical Terms
Backslope : The hillslope profile position that forms the steepest and generally linear, middle portion of the slope. In profile, backslopes are commonly bounded by a convex shoulder above and a concave footslope below. They may or may not include cliff segments (i.e. free faces). Backslopes are commonly erosional forms produced by mass movement, colluvial action, and running water. Compare - summit, shoulder, footslope, toeslope. GSST & HP